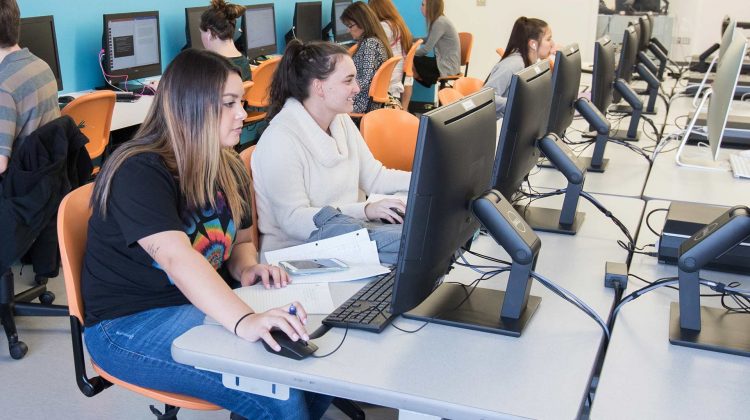
The world celebrates digital access and inclusion with Global Accessibility Awareness Day (GAAD) on the third Thursday of May every year. More than one billion people worldwide have disabilities and impairments. GAAD gets people talking, thinking and learning about digital access and inclusion.
Creating accessible digital content is a must at Missouri State University. We know it can be a lot to think about, so here are some tips to keep in mind. We’ve also included some ways to join in virtually.
#SpotlightAccessibility – Spread positivity around accessibility by highlighting a great feature or product and learn about what others are using.
People with disabilities say these issues come up most often.
- Videos that are missing captions.
- Motion, animations and cluttered pages.
- Auto play videos and auto-advancing slideshows.
- Walls of text (long paragraphs and large chunks of text).
- Small font size
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) does not specify a minimum font size requirement.
- Zooming problems: sites frequently break when size is increased by user.
- Low contrasts and image of text: scan of a page of text saved as PDF produces an image of text.
- Bright color schemes: white backgrounds can lead to migraines.
- Relying only on color: this has long been a no-no, but still prevalent.
- Mouse-focused sites: not usable on touch screens and difficult for users with motor impairments.
- Too small touch-targets: thhis is the reason Missouri State University’s 2019 web redesign is so spacious.
- CAPTCHAS: Keep out a lot more than bots.
Here’s what you can do to make your content more accessible.
While some of these items are automatically handled by MSU’s web templates, you still have an impact on many of of these items.
- Don’t create a wall of text. Keep paragraphs to 2-4 sentences.
- Content styled as Intro format should be brief; one or two short sentences plus 1-3 bullets. Anything longer isn’t introductory content.
- Use headings to make an outline of your content.
- Avoid images of text. When necessary, the alt text should contain all text in the image.
- Don’t use heading markup (e.g., h3, h4) to make an “important” statement; consider a Notice Block instead.
- Don’t use bold or italics for an entire sentence.
- Use meaningful text for links; avoid brief abstract terms like read more or click here.
- For web addresses, write descriptive link text.
Make sure you’re following the style guide.
- In time references, use figures with a.m. and p.m throughout. Omit :00.
- Examples: Summer office hours are 9 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. Telephone support is available 2:30-4 p.m. daily.
- In email addresses, capitalize each word. Example: BoomerBear@MissouriState.edu.
- Preferred capitalizations, spelling and usage:
- Phone numbers: use dashes, not periods. Omit parentheses around the area code. 417-836-5000
- Most words beginning with “non” or “post” should be formatted as one word with no hyphen (ex. noncredit, nondegree, nondegree-seeking, postbaccalaureate, postdoctoral, postdoctorate). Post-master’s should be hyphenated.
- Email, not e-mail.
- Use only one space between sentences. Do not use a space at the end of a paragraph or bulleted list item.
- Common Bear terms:
- Bear CLAW
- Bear Line
- BearWear
- BearFare
- BearMail
- BearPass
- Bear Park North (South)
- BoomerMeals
- Bear Breaks